What is a Termite: Understanding the Silent Destroyer
Termites are small, wood-eating insects. They can cause serious damage to buildings.
Understanding termites is important for homeowners and those interested in pest control. These insects live in colonies and work together to feed on wood, which can weaken structures over time. Termites often go unnoticed until significant damage has occurred. Knowing what termites are and how they behave can help you protect your home.
In this post, we will explore the basics of termites, their habits, and the signs of an infestation. This knowledge is crucial for preventing damage and maintaining the integrity of your property. Let’s dive into the world of termites and learn how to keep them at bay.
Introduction To Termites
Termites are small insects known for their wood-eating habits. They are social creatures living in colonies. These colonies can number from hundreds to millions of individuals. Termites play a vital role in nature. But they can also cause significant damage to wooden structures.
Brief History
Termites have been around for over 250 million years. They first appeared during the Permian period. Fossils show that ancient termites lived in large colonies. These colonies were similar to those we see today. Over time, termites have evolved to adapt to various environments. They can be found worldwide, except in Antarctica.
Importance In Ecosystem
Termites are crucial for the ecosystem. They help break down dead plant material. This process recycles nutrients back into the soil. It improves soil health and fertility. Termites also create tunnels that aerate the soil. This helps water and nutrients reach plant roots more easily.
| Role | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Decomposers | Recycle nutrients |
| Soil Aeration | Improve water flow |
| Habitat Creators | Provide homes for other species |
Despite their benefits, termites can be destructive. They can damage wooden buildings, furniture, and crops. Understanding their role in nature helps us manage them better.
Termite Species
Termites are small, social insects known for their wood-eating habits. They live in colonies and play important roles in ecosystems. There are many species of termites, each with unique characteristics and behaviors.
Common Types
There are three main types of termites: subterranean, drywood, and dampwood termites. Subterranean termites live underground and build mud tubes to access food sources. Drywood termites infest dry wood and do not need contact with soil. Dampwood termites prefer moist wood and are often found in decaying wood structures.
Geographical Distribution
Termite species are distributed across various regions worldwide. Subterranean termites are found in many parts of the world, especially in warmer climates. Drywood termites thrive in coastal areas and regions with high humidity. Dampwood termites are common in forested areas with abundant moisture. Different species adapt to specific environments, making them widespread and diverse.
Anatomy Of Termites
Termites are fascinating insects with a complex anatomy that plays a crucial role in their survival. Understanding their physical structure and life cycle helps us grasp how they thrive and why they are such effective decomposers.
Physical Characteristics
Termites have soft, pale bodies, usually measuring between 4 to 15 millimeters. They have three main body parts: the head, thorax, and abdomen. Their heads feature strong, biting mouthparts for chewing wood. Some species also have large mandibles for defense. Termites have straight antennae and beady eyes. Although worker and soldier termites are wingless, reproductive termites have two pairs of wings.
Life Cycle
The termite life cycle begins with the egg stage. Queen termites lay eggs which hatch into larvae. These larvae develop into workers, soldiers, or reproductive termites. Workers maintain the colony, forage for food, and tend to the queen. Soldiers defend the colony from predators with their powerful jaws. Reproductive termites, also known as alates, leave the colony to start new colonies.
After a mating flight, alates shed their wings and pair up to form new colonies. The cycle then begins anew with the queen laying eggs, ensuring the survival and growth of the termite population.
Habitat And Nesting
Termites are fascinating social insects known for their unique habitat and nesting behaviors. These tiny creatures play a vital role in breaking down dead plant material. Understanding their preferred environments and colony structure gives insight into their complex world.
Preferred Environments
Termites thrive in warm, moist environments. They are commonly found in tropical and subtropical regions. These conditions provide the perfect setting for their survival and growth.
Termites need constant moisture to survive. They often build their nests in soil, wood, or other organic materials. This ensures they have access to the moisture they need.
Colony Structure
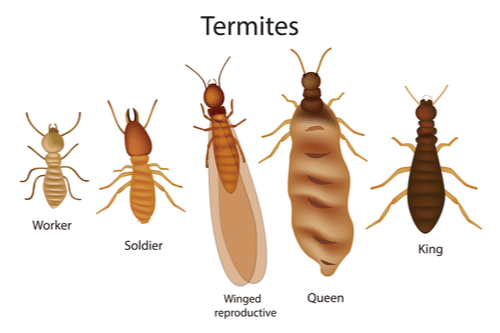
A termite colony is a well-organized system. Each colony consists of three main castes: workers, soldiers, and reproductives.
- Workers: These are the most numerous in the colony. They are responsible for foraging, building, and maintaining the nest. Workers feed and care for the other members.
- Soldiers: Soldiers protect the colony from predators. They have larger heads and strong mandibles to defend the nest.
- Reproductives: This caste includes the king, queen, and alates. The queen’s primary role is to lay eggs. The king mates with the queen. Alates are winged termites that leave the colony to start new colonies.
The termite colony functions like a well-oiled machine. Each caste performs its role to ensure the colony’s survival and growth.
Diet And Feeding Habits
Termites play a significant role in the ecosystem. Understanding their diet and feeding habits helps us appreciate their ecological contributions. This section dives into what termites eat and how they feed, highlighting their importance in nature.
Wood Consumption
Termites are best known for their ability to consume wood. They have specialized microorganisms in their guts that allow them to digest cellulose, the main component of wood. These microorganisms break down the cellulose, providing termites with the necessary nutrients. This makes termites a unique and vital part of the ecosystem.
There are different types of termites, and each type has its preferred wood. For instance, drywood termites consume dry wood, while subterranean termites prefer moist wood. The feeding habits of termites can cause significant damage to wooden structures, making them a concern for homeowners.
Role In Decomposition
Termites play a crucial role in the decomposition of dead plant material. By breaking down wood and other organic matter, they recycle nutrients back into the soil. This process helps maintain soil health and promotes plant growth. Termites contribute to the nutrient cycle, ensuring the sustainability of the ecosystem.
In forests, termites help decompose fallen trees and dead plants. This decomposition process is essential for the health of the forest, as it clears dead material and enriches the soil. Without termites, the accumulation of dead wood would slow down the nutrient recycling process.

Credit: www.terminix.com
Signs Of Termite Infestation
Termites are silent destroyers. They can cause significant damage before you notice. Understanding the signs of termite infestation can save your home.
Visible Indicators
Visible indicators are often the first clues. Look for discarded wings around windows or doors. Termites shed their wings after swarming.
Check for mud tubes on walls or foundations. Termites build these tubes for moisture. They protect them from predators. Wood damage is another sign. Tap on wood. Hollow sounds may indicate termites.
Early Detection
Early detection can prevent severe damage. Listen for quiet clicking sounds. Termites use head-banging to communicate. Inspect wooden furniture and structures. Look for small holes or sawdust-like droppings.
Watch for swollen floors or ceilings. Termites can cause these areas to warp. Keep an eye on your garden. Termites can build nests in soil or mulch.
Impact On Human Structures
Termites are small insects, but they have a huge impact on human structures. These pests feed on wood and other materials, causing significant damage. Understanding their impact can help in taking preventive measures.
Damage To Buildings
Termites can cause serious damage to buildings. They chew through wood, weakening the structure. This can lead to:
- Cracked walls
- Warped floors
- Hollowed wood
Termite colonies can grow very large. A single colony can have millions of termites. They work tirelessly, causing damage 24/7. This can lead to serious structural issues if not addressed.
Economic Costs
The economic costs of termite damage are staggering. In the United States alone, termite damage costs billions each year. Homeowners and businesses spend large amounts on:
- Inspections
- Treatments
- Repairs
Preventive measures are also costly. These include regular inspections and treatments. But, they are necessary to avoid larger expenses in the future. The following table shows the average costs:
| Service | Average Cost |
|---|---|
| Inspection | $100 – $200 |
| Treatment | $500 – $2,500 |
| Repairs | $3,000 – $8,000 |
These costs highlight the importance of early detection and treatment. Ignoring termite damage can lead to even higher expenses over time.

Credit: en.wikipedia.org
Prevention And Control
Termites can be a significant threat to homes and buildings. Proper prevention and control measures are necessary to protect your property. This section covers effective strategies to prevent and control termite infestations.
Preventative Measures
Preventing termites from infesting your home is crucial. Here are some effective preventative measures:
- Eliminate Moisture: Termites thrive in moist environments. Fix any leaks and ensure proper drainage around your home.
- Remove Wood Debris: Keep firewood, lumber, and paper away from your foundation. Termites are attracted to these materials.
- Seal Cracks: Seal any cracks or openings in your home’s foundation and walls. This prevents termites from entering.
- Regular Inspections: Schedule regular termite inspections with a professional. Early detection is key to preventing major infestations.
Treatment Options
If termites have already invaded your home, you need effective treatment options. Here are some common methods:
- Liquid Termiticides: These chemicals create a barrier in the soil around your home. Termites are killed when they come into contact with it.
- Bait Systems: Bait systems use poisoned bait to attract and kill termites. This method targets the entire colony.
- Fumigation: Fumigation involves sealing your home and filling it with a gas that kills termites. This is effective for severe infestations.
- Borate Treatments: Borate is a chemical that can be applied to wood. It prevents termites from feeding on the wood and protects it.
By implementing these measures, you can safeguard your home from termites and keep it safe.
Credit: smarterpestcontrol.com
Frequently Asked Questions
Are Termites Harmful To Humans?
Termites are not harmful to humans directly. They can cause significant damage to wooden structures in homes.
What Do Termites Do?
Termites eat wood, causing structural damage to buildings. They build colonies and tunnels. Termites also decompose dead trees and plants.
Should I Worry If I See A Termite?
Yes, you should worry if you see a termite. Termites can cause significant damage to your home. Contact a pest control professional immediately.
Do Termites Go Away On Their Own?
Termites do not go away on their own. They need professional treatment to eliminate them effectively. Ignoring termites can cause severe damage to your property.
Conclusion
Understanding termites is essential for protecting your home. These tiny insects can cause significant damage. Regular inspections help detect any signs of infestation early. Simple preventive measures can save you from costly repairs. Always stay informed about the habits and signs of termites.
Knowledge is your best defense against these pests. Protect your property by staying vigilant. Thank you for reading!