Where Does Ash Tree Grow? Discover Ideal Habitats
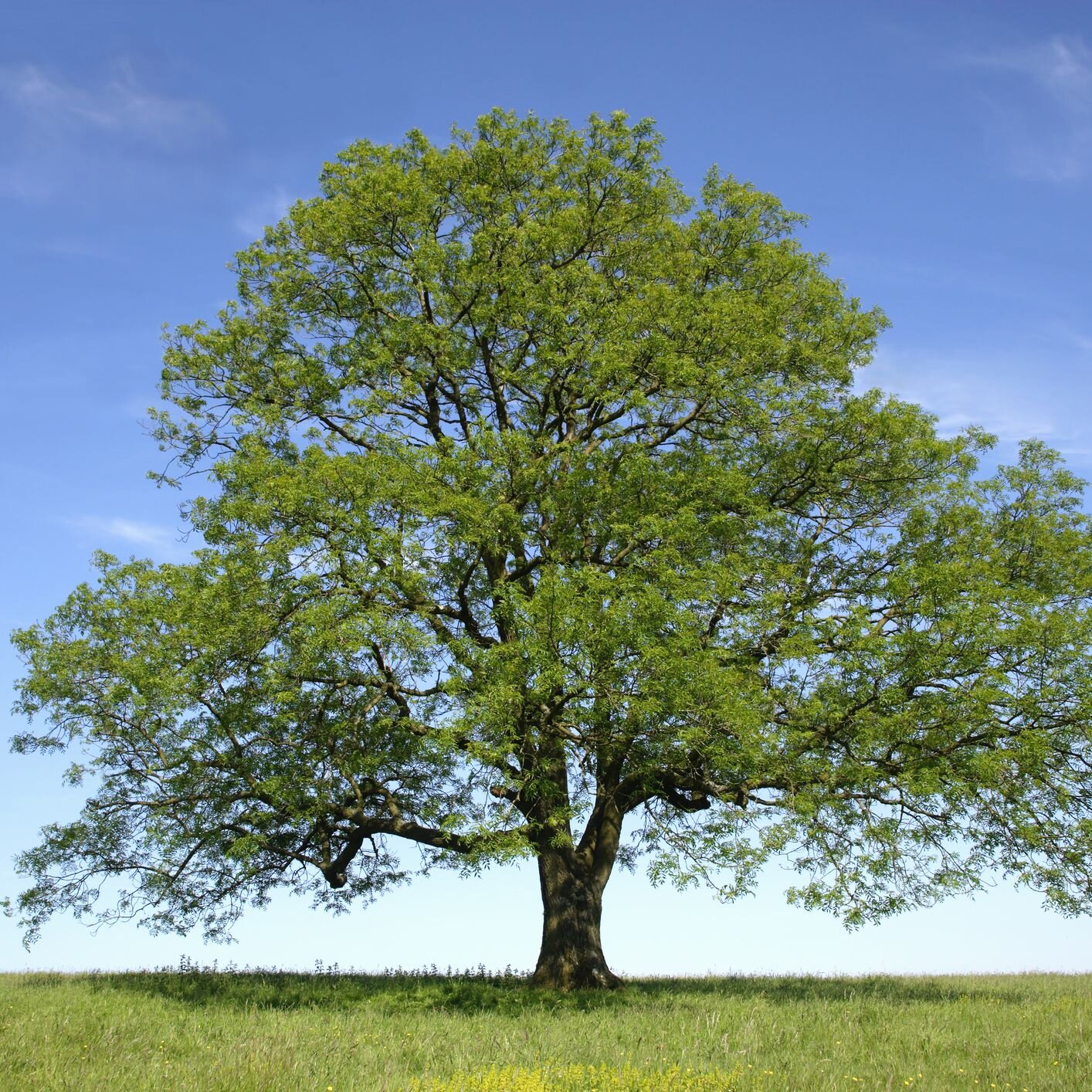
Imagine walking through a serene forest, the sun filtering through leaves, casting gentle shadows on the ground. Among these trees, one stands out with its distinct elegance—the ash tree.
Known for its sturdy wood and graceful form, the ash tree has captured the fascination of many. But where exactly does this majestic tree grow? If you’ve ever wondered about the natural habitats of the ash tree or what makes them thrive in particular environments, you’re in the right place.
This article will unravel the secrets behind the preferred growing conditions of ash trees, revealing why they flourish in certain regions and what you might do if you’re considering planting one in your own backyard. Prepare to be intrigued by the journey of the ash tree, as we delve into its preferred landscapes and discover the reasons behind its widespread presence.

Credit: www.treekc.com
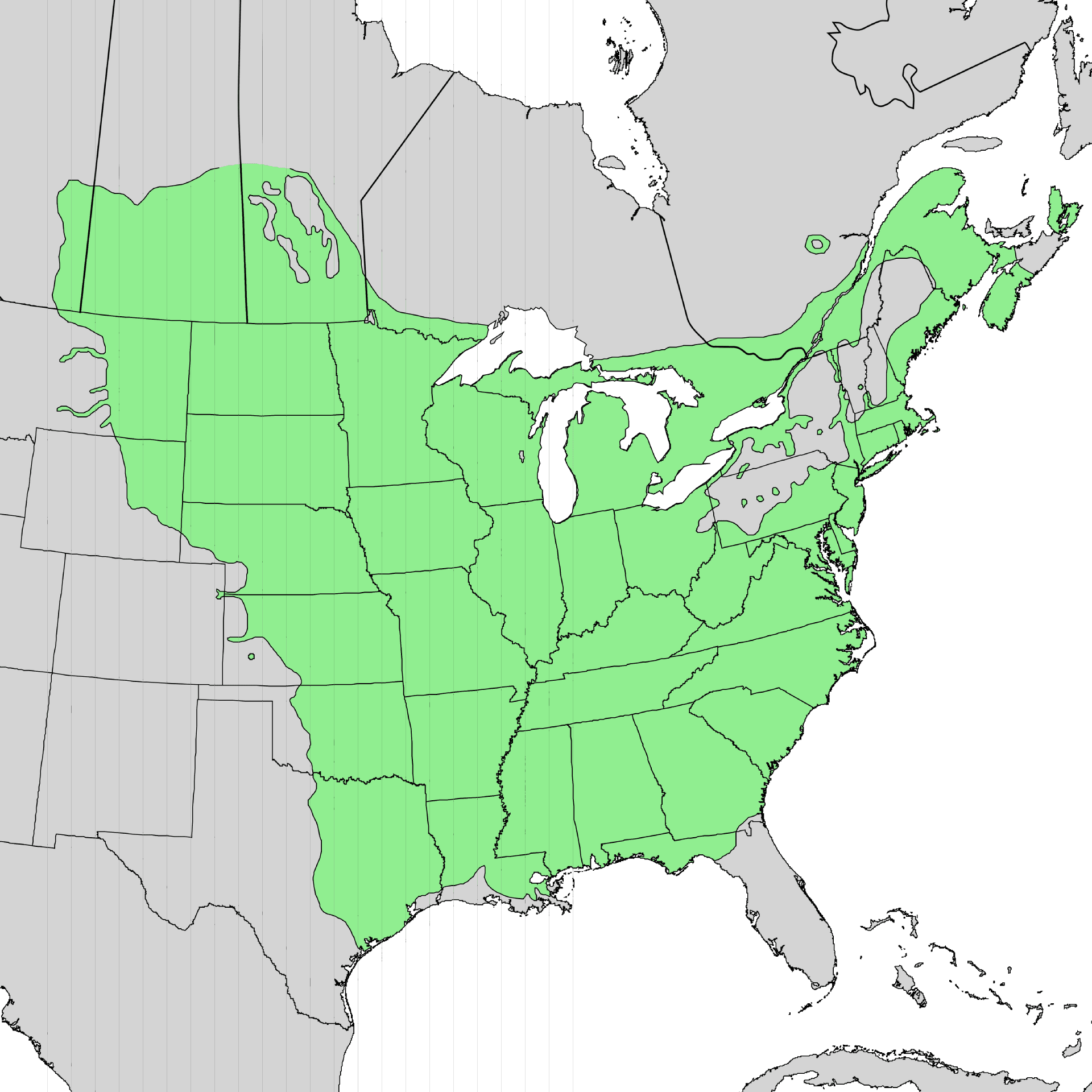
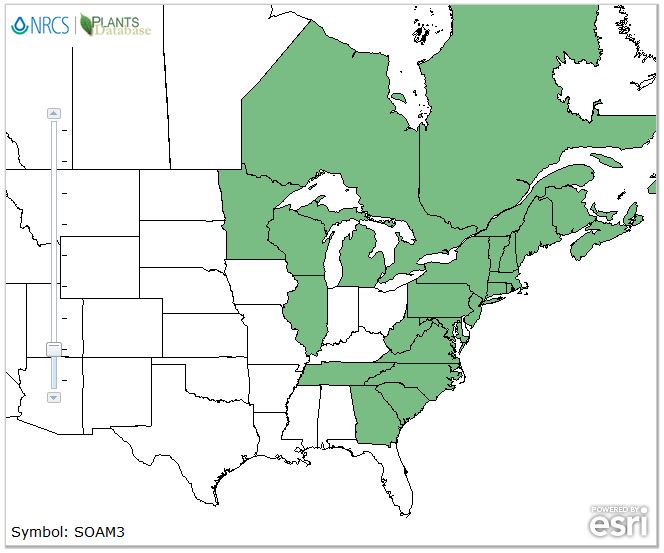
Natural Distribution
Ash trees are common in many parts of the world. They grow mostly in the northern hemisphere. This means they are found in countries like North America, Europe, and Asia. In these regions, they thrive in forests and woodlands. Ash trees prefer areas with plenty of sunlight and well-drained soil. They are often seen along rivers and streams.
In the past, ash trees covered large areas. They were found all over Europe and North America. These trees have been part of forests for many centuries. People used ash wood for making tools and furniture. Its strong wood was very useful. Today, these trees are still important for nature. They provide homes for birds and animals.
Credit: extension.umaine.edu
Climate Preferences
Ash trees like moderate temperatures. They grow well in areas that are not too hot or too cold. They do not like extreme weather. The best temperature for ash trees is between 60 to 70 degrees Fahrenheit. They can survive colder weather, but need protection. They might suffer if the temperature drops too low. Heat can also harm them. It is crucial to find a balance.
Ash trees need adequate rainfall. They prefer areas with regular rain. Dry places are not suitable. Too much rain can cause root problems. They thrive with balanced water levels. It is important for soil to drain well. Wet soil can lead to diseases. Proper irrigation helps them grow strong. Keep an eye on water levels for healthy trees.
Soil Requirements
Ash trees thrive best in loamy soil. This type of soil has balanced sand, silt, and clay. Water drains well here. It keeps roots healthy. Sandy soil is not ideal. It lacks nutrients. Clay soil holds too much water. This can harm the tree.
Ash trees prefer neutral to slightly acidic soil. pH levels between 6.0 and 7.5 are ideal. Low pH can cause nutrient issues. High pH may affect growth. Check soil pH regularly. Adjust if necessary. Use lime to raise pH. Use sulfur to lower it.
Sunlight And Shade
Ash trees need a good amount of sunlight to grow well. They thrive in areas with at least six hours of sun daily. This helps them stay healthy and strong. But ash trees can also grow in places with some shade. They are adaptable and can live in different conditions. Too much shade, though, might make them weak. So, it’s best to plant them in a spot with more sunlight than shade. This ensures they get the energy they need from the sun.
Ash trees have a moderate tolerance for shade. They can survive in shaded areas but won’t grow as fast. Too much shade can limit their growth. The leaves might not be as green and lush. It’s important to balance the amount of sunlight and shade. This balance helps the ash tree grow to its full potential. Finding the right spot is key for the tree’s health.
Elevation Zones
Ash trees thrive in diverse elevation zones, typically found in areas ranging from lowlands to mid-altitudes. These trees prefer well-drained soils and ample sunlight, making them common in forests and urban landscapes. Their adaptability allows them to grow in various environments, contributing to their widespread presence.
Lowland Growth
Ash trees grow well in lowland areas. They like rich, moist soil. These trees can be found near rivers and lakes. Lowlands offer ideal conditions for their growth. They need sunlight and ample space. Ash trees grow tall and strong here. Farmers often plant them in fields. Wildlife finds shelter under these trees. Lowland ash is used for furniture and tools. Its wood is hard and durable.
Mountainous Areas
Ash trees can also thrive in mountainous areas. These trees grow at higher elevations. The air is cooler and cleaner here. They prefer well-drained soil. Ash trees adapt to rocky landscapes. They often grow near mountain streams. Tall peaks provide shelter from harsh winds. Mountain ash wood is valued for crafts and construction. Hikers enjoy their shade during walks. Their leaves change color with seasons.
Human Influence
Ash trees often grow in cities. People plant them along streets. These trees give shade and beauty. Cities need trees for clean air. Ash trees help in many ways. They are strong and can live in crowded places. Urban planting keeps our cities green. It also makes them more beautiful. People love seeing trees outside their windows. Ash trees make that possible.
Farmers use ash trees for windbreaks. They plant them to protect crops. The trees stop strong winds. This helps crops grow better. Ash trees also give shade to farm animals. Animals feel safer and cooler under the trees. Farmers like ash trees for these reasons. The trees are very helpful on farms.
Threats And Challenges
Ash trees face threats from pests like the emerald ash borer. These insects can destroy large numbers of trees. Climate change also poses challenges, affecting their natural growth regions. Protecting these trees is crucial for maintaining biodiversity and forest health.
Pests And Diseases
Ash trees often face threats from pests. The emerald ash borer is a major pest. It damages ash trees quickly. This pest is hard to control. Fungus diseases also harm ash trees. They cause leaves to fall early. Trees become weak and may die. It’s important to protect ash trees from these threats.
Environmental Changes
Environmental changes can affect ash tree growth. Climate change is one major factor. It changes weather patterns. Too much heat or cold can hurt ash trees. Pollution is another problem. It damages leaves and roots. Healthy soil is crucial for ash trees. When soil quality drops, trees struggle to grow. Protecting the environment helps ash trees thrive.
Credit: mauget.com
Frequently Asked Questions
Where Do Ash Trees Grow In The Us?
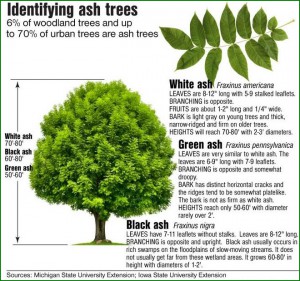
Ash trees grow throughout the United States, thriving in both urban and rural areas. They are commonly found in forests, parks, and residential landscapes. Ash trees adapt well to various soil types and climates, making them widespread across the country.
Popular species include white, green, and black ash trees.
Where Is Ash Commonly Found?
Ash is commonly found in fireplaces, wood-burning stoves, volcanic eruptions, and cigarette trays. It also accumulates from burnt plant material and incinerated waste. Ash serves as a residue from combustion processes and is frequently seen in industrial settings.
What Is So Special About Ash Trees?
Ash trees are valued for their strong, flexible wood and beautiful foliage. They provide excellent shade and support diverse wildlife. Their wood is ideal for making furniture, sports equipment, and musical instruments. Ash trees also have significant ecological importance, contributing to biodiversity and improving air quality.
What Are The Disadvantages Of An Ash Tree?
Ash trees can be prone to pests like the emerald ash borer. They produce messy seeds and weak wood, causing frequent breakage. Roots can damage sidewalks and underground pipes. They require regular maintenance and might not thrive in poor soil conditions.
Conclusion
Ash trees thrive across diverse climates, from Europe to North America. They flourish in regions with well-drained soil and moderate rainfall. Their adaptability makes them a common sight in both urban and rural landscapes. Many appreciate their shade and striking appearance.
These trees play a crucial role in ecosystems, providing habitat for wildlife. Sadly, threats like the emerald ash borer endanger their existence. Conservation efforts aim to protect these valuable trees. Understanding their growth helps in preserving them for future generations.
Let’s cherish and protect ash trees as vital parts of our environment.