Disadvantages of MDF: Why You Should Think Twice
When you’re planning a home improvement project or considering new furniture, you might come across MDF, or Medium-Density Fiberboard. It’s a popular material thanks to its affordability and versatility.
But before you dive into using MDF for your next project, it’s crucial to understand its downsides. You deserve to make informed decisions that ensure your investments last, and knowing the potential pitfalls of MDF can prevent future headaches. By exploring the disadvantages of MDF, you can avoid costly mistakes, ensure the safety and durability of your projects, and choose materials that truly meet your needs.
Are you ready to discover what might be lurking beneath the smooth surface of MDF? Keep reading to find out more.
What Is Mdf?
MDF stands for Medium Density Fiberboard. It is a type of wood product. Wood fibers are combined with glue. They are then pressed into sheets. MDF is smooth and easy to cut. People use it for making furniture. It is also used in cabinets and doors.
MDF is not real wood. It is made from wood waste. This makes it cheaper than solid wood. It has a uniform texture. The surface is flat and smooth. This makes it easy to paint. MDF is popular for its low cost and versatility.
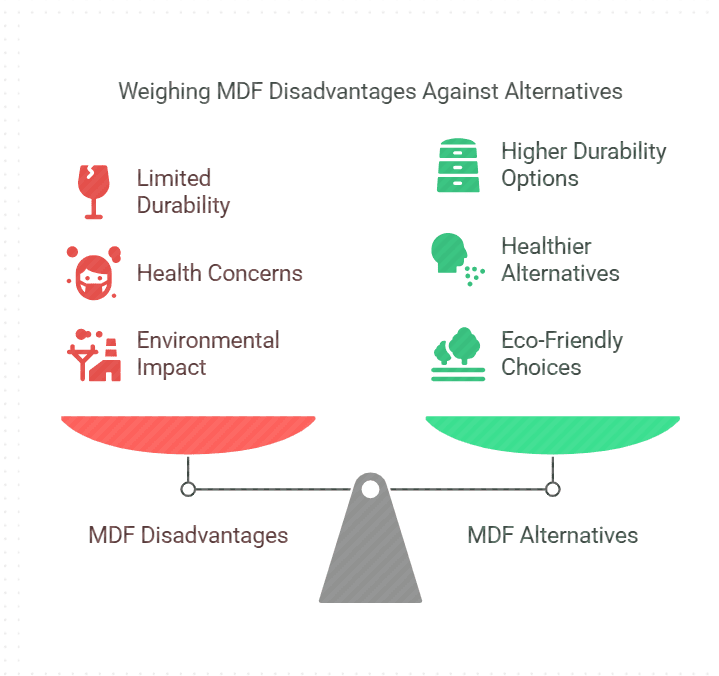
It is important to note MDF’s weaknesses. It can swell when wet. It is not very strong compared to real wood. Heavy objects can cause it to sag. MDF is also heavy. This makes it hard to move. It can also produce dust when cut. This can be harmful if inhaled.
Limited Durability
MDF is prone to moisture damage. Water can make it swell and crumble. This makes MDF a poor choice for bathrooms and kitchens. Humidity can weaken MDF, causing it to lose shape. It’s not as strong as solid wood. MDF can break easily under pressure. It has low resistance to impacts. Long-term use can lead to wear and tear.
MDF absorbs water quickly. Paint or seal MDF to protect it. Without protection, it can rot. Moisture causes swelling and warping. This affects the structure. MDF can be a bad choice for outdoor use. Humidity affects its stability. It is less reliable in wet places.
MDF lacks strength. It cannot hold heavy weight. Screw holes can widen easily. This reduces its hold. Hard impacts can break MDF. It has low tensile strength. Not suitable for load-bearing structures. MDF may sag over time. It’s less durable than plywood.
Health Concerns
MDF can release a gas. This gas is called formaldehyde. It comes from the glue used in MDF. Breathing this gas can be harmful. It can cause eye and throat irritation. Some people might feel dizzy or sick. Long-term exposure is more serious. It might increase cancer risk. Using MDF furniture in well-ventilated areas helps. Keeping windows open can reduce the gas levels.
Cutting or sanding MDF creates a lot of dust. This dust can be bad for your lungs. Breathing it may cause coughing and sneezing. Wearing a mask is important when working with MDF. Dust can also irritate your skin. It might cause rashes or itching. Cleaning up the dust quickly is a good idea. Regular cleaning keeps the air safer.
Environmental Impact
MDF contains non-biodegradable materials. These materials do not break down easily in nature. It takes many years for them to decompose. This can harm the environment. Animals and plants can be affected. Landfills fill up faster with such waste. It is a big concern for our planet.
Making MDF uses a lot of energy. Factories need to use machines and tools. These machines run on electricity and fuel. This means more pollution in the air. The earth’s resources are used up. It adds to the problem of global warming.
Challenges In Repair And Maintenance
MDF is not easy to fix. It can swell or crack easily.
This makes repairs tough. Wood glue might not work well on it.
Holes or dents in MDF are hard to cover.
It needs special care when damaged.
Regular tools might not be enough.
Sanding MDF is tricky. It can make the surface rough.
Paint or coating might not stick well.
Scratches are hard to hide.
Restoring the surface can be a challenge.
It might need complete replacement.
Cost Implications
MDF can seem cheap at first. But costs add up over time. It is not very strong. So, it breaks easily. You might need to replace it often. Replacing things costs money. Over time, this can be a lot. Wood is stronger than MDF. So, wood lasts longer. That means you might spend less. MDF also gets damaged by water. Water can make it swell and break. This means it is not good in wet places. You might need to buy special coatings to protect it. These coatings add to costs too. Think carefully before choosing MDF. It might not be as cheap as you think.
MDF wears out fast. It is not as strong as real wood. So, it does not last long. Things made of MDF can break. Then, you need to buy new ones. This means spending more money. If you want furniture to last, MDF is not the best choice. Many people find they need to replace MDF items often. This is because they get damaged easily. Scratches and dents happen quickly. So, think about how often you want to replace things. Spending a little more on better material might save money in the end.
Alternatives To Mdf
Solid wood is strong and durable. It lasts a long time. Many people like its natural look. Solid wood can be sanded and refinished. This makes it a good choice for many projects. It also has a warm feel. But it can be more costly than MDF. Still, its benefits are many. Choosing solid wood means choosing quality.
Plywood is another good choice. It is made of thin wood layers. These layers make it strong. Plywood is often used for furniture and cabinets. It holds screws well and does not crack easily. It also resists warping. This makes it a good alternative to MDF. Plywood is also lighter than solid wood. It can be less expensive too. Many people like its balance of strength and cost.

Credit: www.ewaywood.com
Frequently Asked Questions
What Are Mdf Advantages And Disadvantages?
MDF offers smooth surfaces perfect for painting and easy customization. It’s affordable and resistant to warping. However, it lacks natural wood strength and can swell with moisture exposure. MDF’s weight makes it difficult to handle and may release formaldehyde emissions.
When Should You Not Use Mdf?
Avoid MDF in damp or humid environments as it swells and weakens. Don’t use for heavy load-bearing applications.
Is Mdf Better Than Plywood?
MDF offers smooth surfaces and is cheaper, ideal for painted finishes. Plywood is stronger and more durable, suitable for structural projects. Choose MDF for aesthetics and plywood for strength.
Does Mdf Damage Easily?
MDF can be prone to damage, especially from moisture or heavy impact. It’s less durable than solid wood. Proper care and maintenance extend its lifespan. Protect from water exposure and handle gently to minimize damage risks. Regular cleaning and sealing improve its resistance against wear and tear.
Conclusion
MDF has its drawbacks, which can impact your projects. It’s not as durable as solid wood. Moisture can damage MDF, causing swelling and warping. Heavy weight makes it hard to move and install. Limited lifespan means it might not be the best for long-term use.
Health risks arise from dust during cutting. It’s crucial to weigh these disadvantages against your needs. Consider other materials if durability and moisture resistance matter. Understanding these drawbacks helps in making informed choices for your woodworking projects. Always think about the right material for your specific needs.