Is Birch Plywood Strong Strength Test Explained
Many people wonder, “Is Birch Plywood Strong? Strength Test Explained.” It can seem a bit confusing when you’re just starting out with woodworking or DIY projects. What makes one wood stronger than another, and how do you actually test it?
Don’t worry, we’ll make it super simple. This guide breaks down everything you need to know about birch plywood’s strength. We’ll walk through what it means and how to tell for yourself.
Get ready to understand birch plywood like never before!
Understanding Birch Plywood Strength
This section explores the core of what makes birch plywood a popular choice for many projects. We will look at its inherent properties and why these matter for its strength. Understanding these fundamentals is key to appreciating why birch plywood performs as it does under stress.
This part sets the stage for why a strength test is even relevant.
What is Birch Plywood
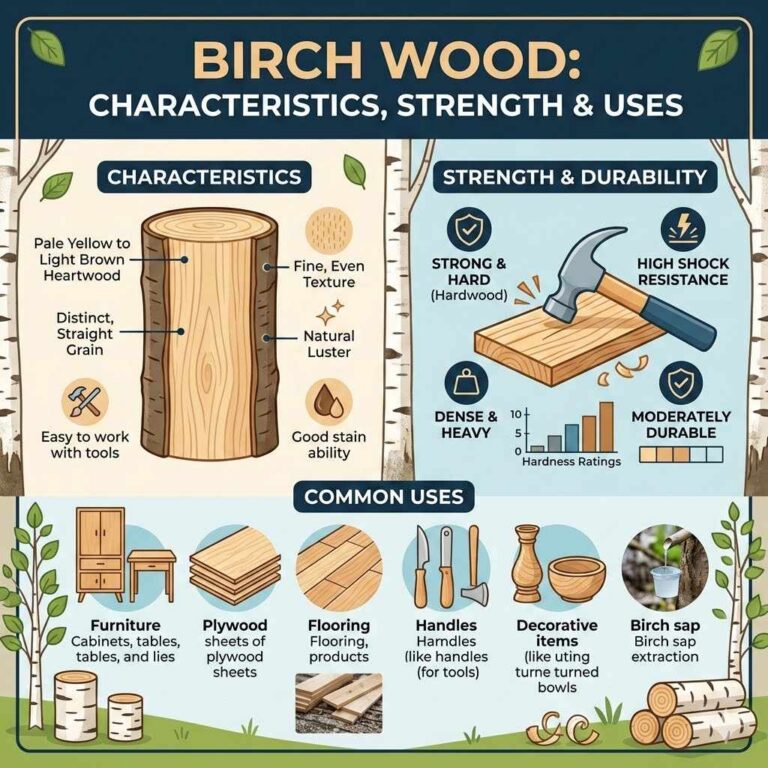
Birch plywood is made from thin layers, called veneers, of birch wood. These layers are glued together with their grain running in different directions. This cross-graining makes the wood much stronger and more stable than solid wood.
It also helps prevent warping and cracking. Birch wood itself is known for its hardness and density, which are great qualities for strong plywood.
The number of layers, or plies, can vary. More plies generally mean a stronger and more rigid panel. The type of glue used also plays a role in its overall durability and resistance to moisture.
Different grades of birch plywood exist, affecting both appearance and strength. Understanding these variations helps in choosing the right panel for a specific job.
Key Strength Properties
Several properties contribute to birch plywood’s strength. Its tensile strength is how much it can be stretched before breaking. Its compressive strength is how much weight it can hold before crushing.
Shear strength is its ability to resist forces that try to slide one layer over another.
Flexural strength is its resistance to bending. This is very important for shelves or panels that will hold weight. Impact resistance is how well it handles sudden blows.
The way the veneers are layered is critical. Alternating the grain direction in each layer creates a balanced structure. This balance distributes stress evenly across the panel, preventing weak spots.
Why Strength Matters
Knowing how strong birch plywood is helps you pick the right material for your project. If you’re building shelves, you need plywood that won’t sag or break under the weight of books. For furniture, it needs to withstand daily use.
In construction, it might be used for subflooring or wall sheathing, where it must support significant loads.
Good strength also means the material will last longer. It resists damage from screws pulling out or nails bending. Choosing appropriate plywood ensures your projects are safe and durable.
It saves you money in the long run by avoiding premature failure and repairs.

Is Birch Plywood Strong A Strength Test Explained
This section directly addresses the question: “Is Birch Plywood Strong? Strength Test Explained.” We will break down what a strength test involves, how it’s done, and what results typically show for birch plywood. This will give you a clear picture of its capabilities and why it’s often considered a strong option.
Types of Strength Tests
Strength tests for plywood usually involve applying force to a sample piece until it fails. Common tests include bending tests, where a panel is supported at two points and a load is applied in the center. This measures its flexural strength and stiffness.
Another test is a shear test. This involves placing a sample between two plates and applying force to slide them past each other. This checks the strength of the glue bonds between the plies.
Tensile tests pull a sample apart to measure its resistance to stretching. These tests are usually done in labs with specialized equipment.
For practical purposes, you might perform simpler tests. You can stack weights on a piece of plywood supported at its ends. You can also try to break a small sample by bending it or striking it.
These give a general idea, though not precise scientific data.
Interpreting Test Results
When you see strength test results, they are often measured in pounds per square inch (PSI) or Newtons per square millimeter (N/mm²). For example, a bending strength might be reported as 7,000 PSI. This means the material can withstand up to 7,000 pounds of force on every square inch before breaking.
Results will vary based on the thickness of the plywood, the number of plies, the type of wood used for the core, and the quality of the glue. Thicker plywood with more plies will generally score higher. Higher numbers mean stronger, more rigid material.
When comparing birch plywood to other types, like pine or poplar plywood, you’ll often see birch performing very well. It typically has higher values for bending and shear strength due to the inherent density and uniform structure of birch wood.
Birch Plywood in Practical Applications
Birch plywood is widely used for cabinetry, furniture, and even in some structural applications. Its strength and smooth surface make it ideal for cabinet doors and drawer boxes that need to hold up to daily use.
In furniture making, it’s used for tabletops, chair seats, and structural components. Its ability to resist bending makes it a reliable choice for shelves that carry heavy items. The consistent quality of birch plywood also makes it a favorite for CNC routing and laser cutting projects because it yields clean edges.
For example, a common use is in making kitchen cabinets. The cabinet sides and shelves need to be strong enough to hold dishes, pots, and pans. Birch plywood can handle this load without sagging, especially when properly supported.
It also offers a good base for finishes like paint or veneer.
Another example is in the construction of acoustic guitar backs. The plywood needs to be strong enough to withstand string tension yet resonant enough to produce good sound. High-quality birch plywood meets these demanding requirements.
A simple scenario: imagine building a workbench. You need a strong, flat surface. Using 3/4-inch birch plywood for the top means it can handle heavy tools and materials without flexing.
The strength ensures the workbench remains stable and safe for demanding tasks.
Statistics show that good quality birch plywood can have a modulus of rupture (a measure of bending strength) of over 8,000 PSI. Its stiffness, measured by the modulus of elasticity, is typically around 1.2 million PSI. These figures place it among the stronger plywood options available.
Factors Affecting Plywood Strength
The strength of any plywood, including birch, isn’t just about the wood itself. Several other factors come into play that can significantly influence how it performs under stress. Understanding these will help you make better choices and interpret strength ratings more accurately.
Wood Species and Core Quality
While we are focusing on birch, it’s important to remember that the core layers of plywood can sometimes be made from other wood species. Even in “birch plywood,” the core might contain other woods like poplar or pine, especially in less expensive grades. These core woods can affect the overall strength.
Dense hardwoods like birch offer superior strength and stiffness. Softer woods might be used to reduce cost, but this can compromise strength. The quality of the veneer itself matters too.
Are there knots or voids? These can create weak points.
High-quality birch plywood uses 100% birch veneers throughout. This ensures consistent hardness and strength from face to core. Lower grades might use a less dense veneer for the inner layers.
This can lead to lower bending strength and stiffness compared to all-birch panels.
Number of Plies and Thickness
The thickness of the plywood panel is a direct factor in its strength. A 3/4-inch thick panel will naturally be much stronger and stiffer than a 1/4-inch thick panel of the same wood. More thickness means more material to resist forces.
The number of plies is also very important. A panel with more layers, even if the total thickness is the same, can be stronger. Each ply adds to the panel’s rigidity.
For instance, a 5-ply 1/2-inch panel might be stronger than a 3-ply 1/2-inch panel. The cross-banding of the plies is what creates this strength.
A common misconception is that “plywood is plywood.” However, the construction makes a huge difference. A 13-ply birch panel is significantly stronger and more stable than a standard 3-ply pine panel of the same thickness. This is because the extra layers provide more resistance to bending and cracking.
Adhesives and Manufacturing Process
The glue used to bond the veneers together is critical to the plywood’s strength and durability. Common adhesives include urea-formaldehyde (UF) and phenol-formaldehyde (PF). PF glues are generally stronger and more water-resistant than UF glues.
The manufacturing process ensures that the glue is evenly applied and the veneers are pressed together under high heat and pressure. This creates a strong, solid bond between the layers. A poor bond can lead to delamination, where the layers start to separate, significantly weakening the panel.
Marine-grade plywood, for example, uses waterproof glues and often has higher quality veneers throughout to ensure maximum strength and resistance to moisture damage. While not all birch plywood is marine grade, the quality of its adhesive is a key indicator of its overall performance.
Environmental Factors
Exposure to moisture, extreme temperatures, and UV light can degrade plywood over time. Moisture can cause the wood fibers to swell and the glue bonds to weaken, leading to delamination and reduced strength.
Constant exposure to high humidity can lead to the edges swelling and the panel becoming less stable. Similarly, very dry conditions can cause shrinking. Extreme heat can weaken the adhesive over time.
Proper storage and finishing are important. Keeping plywood dry and protected from the elements will help maintain its strength and integrity for years. Applying a good sealant or finish can also provide a barrier against moisture.
Comparing Birch Plywood to Other Materials
To truly appreciate the strength of birch plywood, it’s helpful to compare it with other common woodworking materials. This comparison will highlight its advantages and where it stands in the material hierarchy for strength and durability.
Birch Plywood vs. Other Plywood Types
Compared to pine plywood, birch plywood is generally denser, harder, and stronger. Pine is a softwood, making pine plywood lighter and easier to work with but less resistant to dents and scratches. Birch, a hardwood, offers superior strength and a smoother surface.
Poplar plywood is another option. Poplar is also a hardwood, but it’s typically less dense than birch. This means birch plywood will usually have higher load-bearing capabilities and stiffness.
For applications where extreme durability and moisture resistance are paramount, marine-grade plywood often outperforms standard birch plywood, but at a higher cost. However, for most general woodworking and furniture projects, high-quality birch plywood offers an excellent balance of strength, stability, and cost.
Birch Plywood vs. Solid Wood
Solid wood can be very strong, but it is also prone to warping, twisting, and cracking as humidity levels change. Plywood, with its cross-banded construction, is much more dimensionally stable. This means it stays flat and true even with fluctuations in temperature and humidity.
For example, a large solid wood tabletop might require complex joinery to prevent warping over time. A birch plywood tabletop of the same size will remain flat with much less fuss. However, solid wood can sometimes offer greater shear strength in certain orientations if the grain is aligned perfectly.
Plywood also tends to be more economical for large panels than solid wood of the same quality. Obtaining wide, knot-free boards of solid hardwood can be expensive and challenging.
Birch Plywood vs. MDF or Particle Board
Medium-Density Fiberboard (MDF) and particle board are engineered wood products but differ significantly from plywood. MDF is made from wood fibers mixed with resin and pressed into panels. It’s very smooth and stable but can be heavy and prone to sagging under load, especially at greater spans.
It also does not hold screws as well as plywood.
Particle board is made from wood chips and particles bonded together. It is the least strong and least water-resistant of the engineered wood products. It sags easily and its screw-holding power is poor.
Birch plywood excels over MDF and particle board in terms of strength, stiffness, screw-holding ability, and resistance to moisture. While MDF can be good for painted surfaces or where extreme smoothness is needed, plywood is generally superior for structural integrity and durability in most applications.
| Material | Strength | Stability | Screw Holding | Moisture Resistance | Cost (General) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Birch Plywood | High | Very High | High | Moderate to High (depends on glue) | Moderate |
| Pine Plywood | Moderate | High | Moderate | Moderate | Low to Moderate |
| Solid Wood (Hardwood) | High (Variable) | Moderate (Prone to warping) | High | Moderate | High |
| MDF | Moderate (Prone to sagging) | Very High | Low to Moderate | Low | Low to Moderate |
| Particle Board | Low (Prone to sagging) | High | Low | Very Low | Very Low |
Making The Most of Birch Plywood
Now that we’ve explored “Is Birch Plywood Strong? Strength Test Explained,” you can see it’s a robust material. Knowing its strengths and how to use it effectively will help you achieve great results.
This part gives you practical tips for working with birch plywood to ensure your projects are both strong and beautiful.
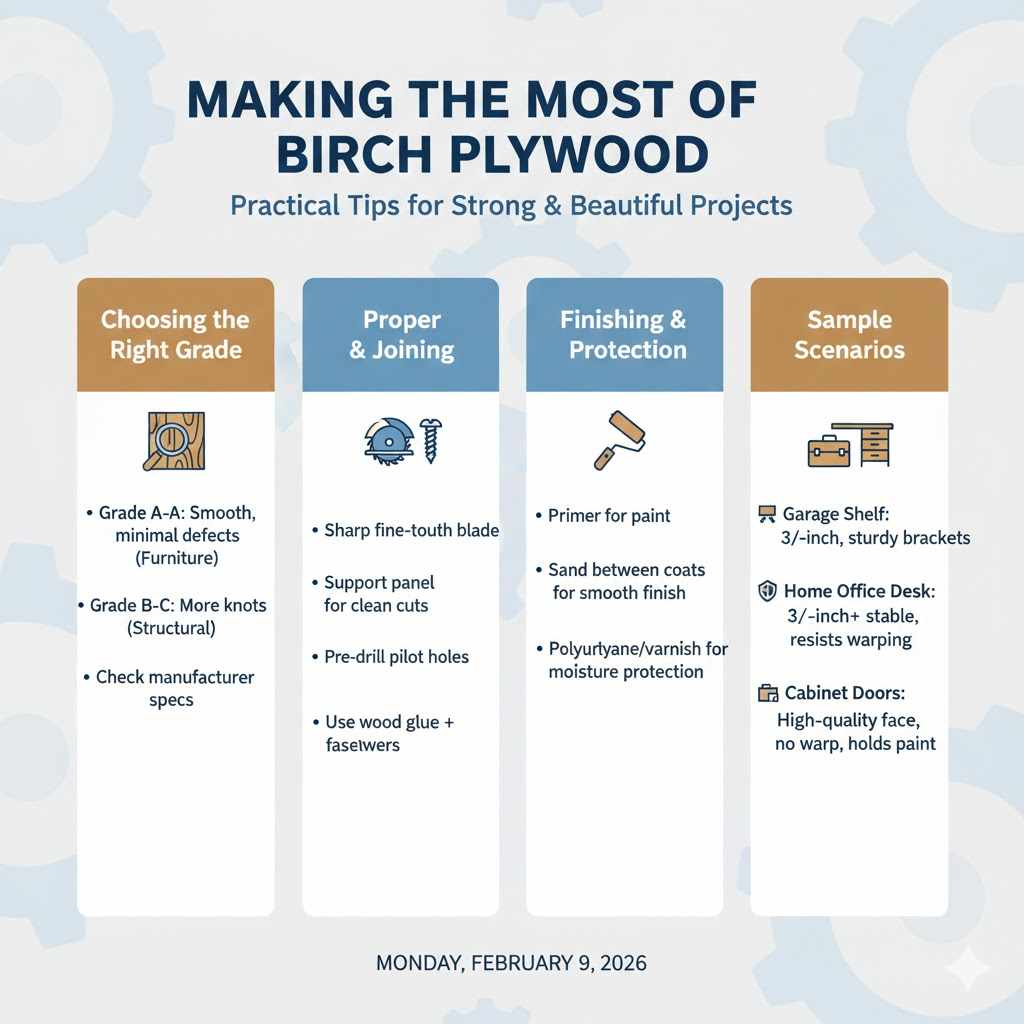
Choosing the Right Grade
Birch plywood comes in different grades, often indicated by letter combinations (e.g., A-A, B-C, I-3). The first letter usually describes the face veneer quality, and the second describes the back veneer. ‘A’ is generally the highest quality, meaning a smooth, sanded surface with minimal imperfections.
‘C’ might have more knots and imperfections.
For projects where appearance is key, like furniture or cabinet fronts, choose grades with good face veneers (e.g., A-A, A-B). For structural components where appearance is less critical, grades like B-C might be sufficient and more cost-effective. Always check the manufacturer’s specifications for any specific strength ratings or intended uses.
Proper Cutting and Joining
When cutting birch plywood, use sharp saw blades to prevent splintering and chipping, especially on the face veneer. Using a fine-tooth blade and a scoring cut can help achieve clean edges. Always support the panel well to prevent sagging during cuts.
For joining, birch plywood holds screws and nails very well. Pre-drilling pilot holes is recommended, especially near the edges, to prevent splitting. Using wood glue in addition to fasteners will create a stronger joint.
For applications requiring high strength, consider using pocket screws, dowels, or biscuits for joinery.
Finishing and Protection
Birch plywood takes finishes very well. For painting, a good primer is essential. For staining or clear coats, the smooth, uniform surface of birch allows for an even application.
You might want to sand lightly between coats to achieve a very smooth finish.
Protecting the plywood from moisture is crucial for its longevity. Apply a durable finish like polyurethane, varnish, or lacquer to seal the wood. This will help prevent swelling and protect against spills and wear.
Sample Scenarios
- Building a heavy-duty shelf for a garage to store tools: Use 3/4-inch birch plywood. Ensure it’s well-supported with sturdy brackets. The strength of the plywood will prevent sagging under the weight of tools.
- Creating a desk for a home office: A 3/4-inch or even 1-inch thick birch plywood top offers a stable and durable surface for your computer and work materials. Its resistance to warping means it will remain flat over time.
- Making cabinet doors: Use a high-quality birch plywood with a smooth face veneer. This will provide a strong, stable door that won’t warp and will hold paint or stain beautifully.
Frequently Asked Questions
Question: Is birch plywood strong enough for structural applications
Answer: Yes, high-quality birch plywood, especially thicker panels like 3/4-inch or more, can be very strong and is suitable for many structural applications like subflooring, wall sheathing, or furniture framing, provided it meets local building codes and design specifications.
Question: How does birch plywood’s strength compare to regular plywood
Answer: Birch plywood is generally stronger and more rigid than standard pine or fir plywood because birch wood is denser and harder. This means it can typically support more weight and is less likely to bend or break.
Question: What makes birch plywood stronger than solid wood
Answer: While solid wood can be strong, birch plywood’s strength comes from its cross-banded construction. This layering distributes stress evenly, making it more stable, resistant to warping, and less prone to cracking than solid wood, especially in large panels.
Question: Can I use birch plywood outdoors
Answer: Standard birch plywood is not recommended for direct outdoor use as moisture can degrade the glue bonds and wood. For outdoor projects, you would need marine-grade plywood or specific exterior-rated engineered wood products.
Question: What is the best way to test birch plywood strength at home
Answer: A simple home test could involve supporting a piece of plywood at both ends and placing progressively heavier weights in the center to see when it starts to bend or fail. However, this is a qualitative test and not a precise scientific measurement.
Summary
Birch plywood is indeed strong, thanks to its dense hardwood construction and layered design. Strength tests confirm its excellent bending, shear, and impact resistance. Its stability, compared to solid wood, makes it a reliable choice for projects needing durability.
Choosing the right grade and finishing it properly ensures it performs at its best.