Helical Vs Spiral: Unraveling the Key Differences
Are you curious about the differences between helical and spiral shapes? These terms often pop up in various fields, from architecture to engineering, and even in nature.
Understanding their distinctions can help you make informed decisions, whether you’re designing a product or simply expanding your knowledge. Imagine how these shapes influence strength, aesthetics, and functionality in everyday applications. By the end of this article, you’ll not only grasp the fundamental differences but also uncover how these shapes impact your life in ways you might not expect.
Dive in to discover how the seemingly subtle variances between helical and spiral can lead to profound effects in design and nature.
Helical And Spiral Shapes
A helical shape looks like a spring or a coil. It twists and turns in a regular pattern. A spiral shape also twists, but it usually gets bigger or smaller as it turns. Both shapes are common in nature. Think of DNA for helical and snail shells for spiral.
Helical shapes have even turns and distances. Spirals may have tight or wide turns. Helical structures are often seen in machines. Spirals are often seen in plants and animals. Helices remain the same size throughout. Spirals grow or shrink as they turn.

Credit: freewayfasteners.blogspot.com
Historical Context
Nature gives us many shapes. Both helical and spiral forms are seen everywhere. Plants and shells are examples. Helical shapes twist and turn. Spirals grow outward in circles. These shapes have been around for millions of years. They are simple yet beautiful. Nature uses them in clever ways.
Designers use these shapes. They have changed over time. The helical shape is used in staircases. It saves space. Spirals are seen in art. They make patterns and are pleasing to the eye. Engineers also use them. They help in making strong structures. These designs are both practical and pretty.
Applications In Technology
Helical designs are used in making stairs and ramps. They give smooth curves. Engineers use them for buildings with modern looks. Spiral shapes are often seen in bridges. They help in spreading weight evenly. These shapes also make structures stronger. Architects love using them for unique designs. Both shapes are important. They help in making safe and beautiful buildings.
Helical structures are found in DNA models. They are also in some medical tools. These tools can bend easily. Spiral shapes are used in springs. They help in making devices flexible. Doctors use devices with these shapes. It makes surgeries more accurate. These shapes are vital in medical equipment. They improve the function of tools.

Credit: www.konetool.com
Mathematical Concepts
Helical shapes twist like a screw. They have a circular base. Spiral shapes wind outward like a snail’s shell. They have a curved path. Helices rise steadily and do not cross themselves. Spirals increase outward from the center.
Helices are often seen in springs. Spirals are found in nature like in seashells. Helices and spirals are both 3D shapes. But they are not the same. Helices have a regular pattern. Spirals can be more random.
Helical shapes use the cylinder formula. Radius and pitch are needed. Pitch is the height of one turn. Spirals use the Archimedean spiral formula. This involves the radius and angle.
Helices need trigonometry for calculations. Sine and cosine help find points on the helix. Spirals involve polar coordinates. They use radius and angle for calculations.
Role In Art And Culture
Both helical and spiral shapes carry deep meanings in art. Helical forms are often seen as symbols of growth and progression. They show how things move forward and develop. Spirals can represent the circle of life or continuity. They show how life keeps going and never stops.
Artists use these shapes to tell stories. A spiral might show the endless journey of life. A helix could show how ideas evolve over time. These shapes appear in sculptures, paintings, and drawings. They add depth and meaning to the artwork. Patterns with spirals or helices can catch the eye. They make art interesting and dynamic.

Credit: forums.sketchup.com
Scientific Implications
Helical and spiral shapes both have important roles in science. A helical shape is like a spring. It twists evenly around a center. In science, this shape helps explain the structure of DNA. DNA has a double helix structure. This means two helices twist together. The spiral shape is different. It winds around a point, growing larger. Spiral galaxies are examples of this shape. Understanding these shapes helps scientists. They build theories about the universe and life.
Helical shapes appear in nature. Think of DNA again. It’s a famous helical structure. This shape keeps genetic information safe. Spirals show up too. Snail shells are good examples. They have a spiral design. This helps the snail grow. Both shapes are important for life. They show up in many living things. Studying these shapes helps us understand nature better.
Comparative Analysis
Helical and spiral shapes are common in nature and design. A helical structure looks like a spring. It has a smooth curve. The spiral shape is more like a flat coil. It wraps around a center point. Helical forms are 3D and extend in space. Spirals are often 2D. They lay flat on surfaces. These differences matter in engineering and design.
Helical shapes are strong and flexible. They are often used in springs and DNA. Spirals are easy to store. They are common in notebooks and shells. Each shape has its own benefits. Helical designs can handle pressure well. Spirals save space and can expand easily. Choose the right shape for your needs.
Future Trends
Helical and spiral designs are advancing. New materials make them stronger. Smart technologies help improve efficiency. Designers focus on energy-saving features. They aim to reduce waste.
3D printing is becoming popular. It helps create complex shapes easily. Custom designs are now possible. This opens new doors for creativity. Builders can try new ideas.
Future designs may use self-healing materials. These fix themselves when damaged. This idea is exciting. It could make structures last longer.
Automation will change design methods. Computers make tasks easier. They help find errors fast. This saves time and money.
New technologies bring challenges. Designers need to learn new skills. They must adapt quickly. Changes happen fast in this field.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Is The Difference Between Helical And Spiral?
Helical refers to a three-dimensional spiral shape, like a spring. Spiral is a two-dimensional curve, like a snail shell. Helical structures twist along an axis, while spirals expand outward from a central point. Helixes are often used in engineering, whereas spirals are common in nature and art.
What Is The Difference Between Helical And Spiral Path?
A helical path involves a 3D spiral around an axis, resembling a spring. A spiral path is 2D, moving outward or inward from a central point. Helical paths have depth, while spiral paths are flat. Helical paths are often seen in screws, while spiral paths are visible in whirlpools.
What Is The Difference Between Helical And Spiral Planers?
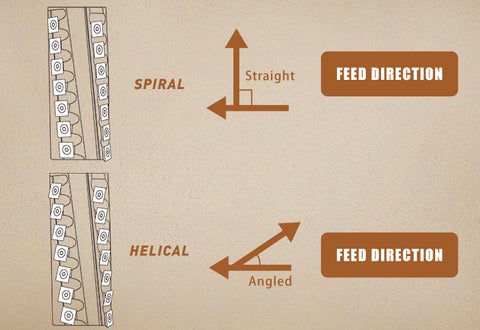
Helical planers use angled knives for smoother cuts and reduced noise. Spiral planers have curved blades arranged in a spiral pattern, offering a finer finish. Both designs minimize tear-out and enhance efficiency in woodworking, making them popular choices for professionals seeking precision and quality.
What Is The Difference Between Helical And Spiral Stairs?
Helical stairs feature a curved shape without a central column. Spiral stairs wrap around a central pole, forming a tight circle. Helical stairs offer a more open appearance and are often used in architectural designs. Spiral stairs are more compact and space-efficient, suitable for small areas.
Conclusion
Choosing between helical and spiral designs depends on your needs. Helical designs offer smoother transitions. Spiral designs provide compact structures. Consider space and function requirements. Both designs have unique advantages. Helical designs excel in stability. Spiral designs shine in flexibility.
Analyze project details carefully. Match design to specific goals. Consult experts for informed decisions. Explore real-world examples for clarity. Understand each design’s impact on efficiency. Maximize benefits with proper implementation. Make informed choices for successful outcomes. Design selection influences project success.
Achieve goals with the right design approach.