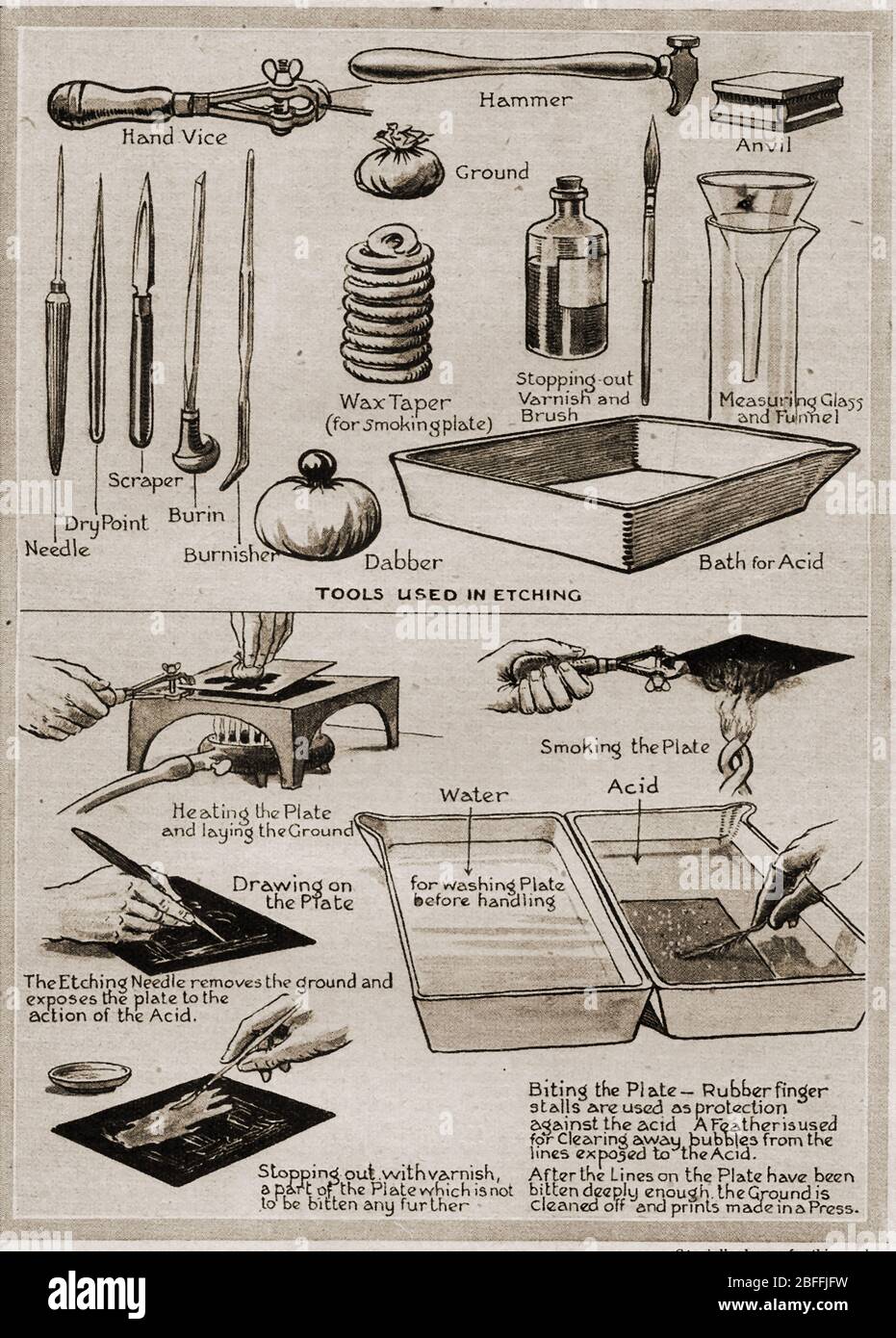
What Tools are Used for Etching: Essential Equipment Guide
Etching is an artistic technique used to create designs on surfaces. This process requires specific tools to achieve the desired results.
Etching, an age-old art form, captivates many with its intricate designs and detailed patterns. Artists and craftsmen use various tools to carve and etch on materials like metal, glass, and wood. These tools, each with a unique purpose, help bring creative visions to life.
Whether you’re a beginner or an experienced artist, understanding these tools is essential. Let’s dive into the world of etching and discover the essential tools used in this fascinating craft. This guide will help you understand the basic tools needed for etching, making your artistic journey smoother and more enjoyable.

Credit: www.artistsandillustrators.co.uk
Introduction To Etching Tools
Proper equipment is vital for good etching. Etching tools help create fine details. Needles, scrapers, and etching presses are common. Acids and mordants create the etch on metal or glass. Each tool has a specific role. Choosing the right one is key.
Using the right tools ensures clean lines. Good tools last longer. They also help achieve better results. Incorrect tools may damage the material. This can ruin the project.
Safety is crucial in etching. Protective gear like gloves and goggles are necessary. Etching involves chemicals. These can be harmful. Ensure good ventilation. Always follow safety instructions. Proper storage of tools and chemicals is also important.
Basic Hand Tools
Needles and scribes are essential for etching. These tools help create fine lines. Needles are used to scratch the surface. Scribes are sharper and can make deeper cuts. They come in different sizes. Each size is used for different details. Both tools must be sharp. A dull tool will not work well.
Burnishers and scrapers are also important. Burnishers smooth the metal. They create a shiny finish. Scrapers remove unwanted material. They clean up rough edges. Both tools are used together. They help make the final piece look polished. Keeping them clean is vital.
Etching Needles
Etching needles come in various shapes and sizes. Some common types include round needles, spade needles, and lozenge needles. Each type serves a different purpose. Round needles are great for fine lines. Spade needles create broader strokes. Lozenge needles are used for varied line widths.
Picking the right needle is crucial. Consider the material you are etching. Some needles work better on certain materials. Also, think about the design you want. Fine details need a sharp, thin needle. Broader designs need a thicker needle. Always test the needle first. This ensures it fits your needs.

Credit: thediningtablestudio.uk
Etching Grounds
Hard ground is a type of resist used in etching. It is applied to the surface of the metal plate. This ground is usually made from a mixture of wax and resin. After application, the artist uses a sharp tool to draw on the plate. The lines created will expose the metal underneath. These lines will be etched by acid later on.
Soft ground is another type of resist. It is more flexible than hard ground. Artists can press textures into it. For example, leaves or fabrics. This creates interesting patterns in the final etching. Soft ground is also made from wax and other materials. It allows for more varied textures. It is often used for more intricate designs.
Acid And Mordants
Etching uses acids to cut into the surface of a material. Nitric acid and hydrochloric acid are often used. Ferric chloride is also popular. Each acid has its own uses. They help in different etching techniques. Nitric acid is strong and fast. Hydrochloric acid is less aggressive. Ferric chloride works well on metals. These acids create fine lines and details. Etchers choose the best acid for their work.
Safety is very important when using acids. Always wear gloves and goggles. Use acids in a well-ventilated area. Keep acids away from children and pets. Store acids in a cool, dry place. Always read the label before using acids. Follow all safety instructions. Clean spills right away. Have a first aid kit nearby. Never mix different acids together. Dispose of acids safely. Your safety comes first.
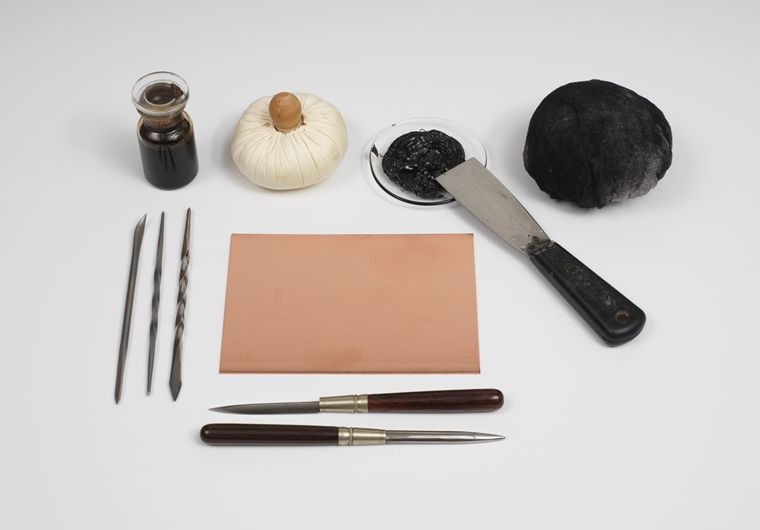

Credit: www.metmuseum.org
Etching Press
Choosing the right etching press is crucial. Consider the size and type of your projects. Smaller presses are good for beginners. Larger presses suit more complex works. Always check the press’s durability. A strong press lasts longer.
Keep your etching press in top shape. Clean it after every use. Dust and dirt can harm the machine. Oil the moving parts regularly. This keeps them running smoothly. Check for loose bolts and screws. Tighten them if needed. Store the press in a dry place. Moisture can cause rust. Regular maintenance ensures your press works well for years.
Aquatint Tools
Rosin is a key tool for aquatint. It creates tiny dots on the metal plate. This helps in making shades and textures. It is a powder that you sprinkle on the plate. Then, heat the plate to make the rosin stick.
Spray paint can also be used. It is a quick and easy method. Spray a fine mist on the plate. Make sure it is even. This helps in creating smooth gradients. Both methods are great for adding depth to the artwork.
First, clean the metal plate. Next, apply rosin or spray paint. Heat the plate if using rosin. Then, dip the plate in acid. The acid bites into the exposed areas. Stop the acid process by rinsing the plate. Finally, ink the plate and print your design.
Advanced Etching Equipment
Photo etching uses light to create designs on metal. A photoresist film covers the metal. Then, a light source shines through a mask onto the film. This hardens the film where light hits. Next, the metal goes into a chemical bath. The bath removes the unexposed film. Acids then etch away the unprotected metal. Common tools include UV light units, masks, and chemical baths.
Electro-etching uses electricity and a saltwater solution. The metal is the anode and a piece of metal is the cathode. A power supply sends electricity through the solution. This removes metal from the anode. Tools needed include a power supply, saltwater solution, anode, and cathode.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Are Common Etching Tools?
Common etching tools include etching needles, burins, and scrapers. These tools help artists create detailed designs on various surfaces.
What Is An Etching Needle Used For?
An etching needle is used to carve intricate designs into a surface. It provides precision and control for detailed work.
How Does A Burin Work In Etching?
A burin is used to incise lines into a metal plate. It allows for deep, clean cuts, essential for etching.
Why Use Scrapers In Etching?
Scrapers are used to remove excess material and refine the etched design. They help achieve smooth and polished finishes.
Conclusion
Etching requires specific tools for best results. Common tools include etching needles, acid baths, and resist materials. Each tool serves a unique purpose. Beginners and professionals alike can benefit from understanding these tools. Practice and patience are key. Experiment with different materials and techniques.
Always prioritize safety while etching. Proper knowledge and tools lead to beautiful designs. With time, skills will improve. Happy etching!